Semaphore is an abstract for controlling access by multiple threads (sessions) to a common resource. Binary semaphore, it can be called Mutex, or Lock/Unlock, allows only one thread access a resource at a time. Back old days, in C++ programming, critical section object is used for this purpose. In C#, keyword lock(obj){code block} and Monitor class implements binary semaphores. Once a object is locked by one thread, other threads who need to acquire the lock on the object will have to wait until the lock on the object is released by thread previously held. SQL Server is an multi-threading application. It uses semaphores internally to control the access to the record, for instance, while you are modify a record, an exclusive lock is placed on the record and released when modification finishes. This is a binary semaphore. In T-SQL, you can implement binary semaphore by locking row(s) and application locks.
 John H
John H
SQL Mail Removed in SQL Server 2012
SQL Mail is removed from SQL Server 2012 as Microsoft promised in SQL 2008’s BOL. Configuration “SQL Mail XPs” is removed from SQL 2012, check sp_configure in SQL Server 2012. Supporting procedures are removed as well. Those procedures are removed from master database xp_startmail, xp_stopmail, xp_findnextmsg, xp_readmail, xp_deletemail, xp_sendmail, and sp_processmail. Ensure your SQL Server … Read more
Locking and Blocking (9) – Live Locks and Deadlocks
Deadlock can happen at latch level, memory, MARS, parallel query, etc. In this post, I am only going to talk about deadlocks at lock level. Resource A and B, when Session 1 locks Resource A and tries to get a lock on Resource B which has a incompatible lock held by Session2, Session 1 will wait until Session 2 releases locks on Resource B. This is called live lock. A live lock will be eventually resolved when the blocking session releases the lock or requesting lock gets timeout. If Session 2 requests a incompatible lock on Resource A at this moment, deadlock happens, because Session 1 will be waiting for the released lock on Resource B and Session 2 will be waiting for the released lock on resource A. Both sessions are deadly locked and blocked. I am going to give you few deadlock scenarios and solutions below.
Run Dynamic SQL within Function
Functions are the most restrictive code blocks you can define in SQL Server. They perform just like stored procedures in which it can return set and output parameters. But you cannot create or modify objects and the data within the object in a function except the objects are table variables and table value type variables. Actually any transaction depended objects are not allowed to run in a function, such as SEND and RECEIVE. You can run exec proc within a function but only some extended procedures are allowed. One is not allowed but most developers(including me) desire is to run sp_executesql in a function. You can get around it by creating CLR functions.
Locking and Blocking (8) – Lock Hints
Lock hints are used to customize the locking behavor of SQL Server from 3 main perspectives, granularity, mode, and duration. Available hints are HoldLock, NoLock, NoWait, PagLock, ReadCommtted, ReadCommittedLock, ReadPast, ReadUncommitted, RepeatableRead, RowLock, Serializable, TabLock, TabLockX, UpdLock, and XLock. A full understanding of them is important before using them. Let’s assume you are running your … Read more
SQL Server Error Log
SQL Server Error Log records information about SQL Server during runtime. It’s created under SQLServerRootFolder\MSSQL\Log folder for each start of SQL Server. Information in the file is varied. Some of them are information only; no action needed to be taken. Some of them are really the information you want to look at. The simplest way accessing it is to use SSMS->Management->SQL Server Logs. Bur when the log is huge, Log File Viewer will retrieve all logs back until hit the end of the log or all your local memory is exhaused. Here is a simple way you can recyle them.
Locking and Blocking (7) – Transaction Isolation Levels
In my first post of the series, I have mentioned that SQL Servers before version 2008 implemented transaction isolation levels by using locking only. In the newer version of SQL Server, this mechanism is NOT changed. Snapshots related isolation levels are the functionalities added to the existing framework. In general, transaction isolation levels controls the reading,SELECT, behaviour of SQL Server. I am going to explain it from locking perspective.
Page Type
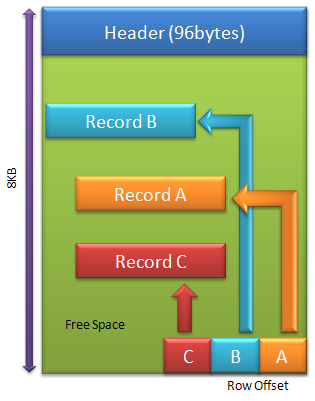 There are different types of pages in SQL Server. No matter what types of pages are, the layout of the page is the same. A data file consists of numbers of 8k-pages. A Page includes 8192 bytes. First 96 bytes are used for header. The rest of the space is for data. A variable length row offset array (or slot array) is located at the end of every page and grows backwards. Count of records (size of array) is saved in the header. The size of each element in the offset array is 2 bytes. Records in a page are not sorted even though it is an index page. If the data needs to be sorted, the offset array will be is sorted by the key of the index.
There are different types of pages in SQL Server. No matter what types of pages are, the layout of the page is the same. A data file consists of numbers of 8k-pages. A Page includes 8192 bytes. First 96 bytes are used for header. The rest of the space is for data. A variable length row offset array (or slot array) is located at the end of every page and grows backwards. Count of records (size of array) is saved in the header. The size of each element in the offset array is 2 bytes. Records in a page are not sorted even though it is an index page. If the data needs to be sorted, the offset array will be is sorted by the key of the index.
As far as I know, there are about 14 types of pages in SQL Server data file.
- Type 1 – Data page.
- Data records in heap
- Clustered index leaf-level
- Location can be random
- Type 2 – Index page
- Non-clustered index
- Non-leave-level clustered index
- Location can be random
TechDays Canada 2011 – Vancouver BC, Nov 15 and 16.
TechDays Canada 2011 – Vancouver Nov 15 and 16 I am going to present “The T-SQL Cookbook: What’s Cool in Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 and New in SQL Server 2012” at TechDays 2011 Vancouver 1:00PM 16, 2001, http://www.microsoft.com/canada/techdays/2011/. I will talk about new programming features introduced in SQL Server 2012 in the session. Ok, … Read more
Locking and Blocking (6) – NoLock
Nolock table hint tells SQL Server engine to not place locks to rows and/or pages while reading them. With this hint enabled, query will not be blocked by any row level modification. It’s equivalent to READUNCOMMITTED table hint in which it allows query return uncommitted data. Many people probably already know that schema stability lock will be applied to the table being access with this table hint, but it’s not always the trueth. In some cases, it will apply Shared lock to the HOBT — partition.
